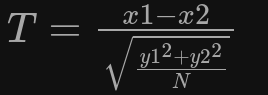slides.md 11 KB
title: CPA Angriff auf Speck author: Robin Dietrich & Marius Schwarz
data: 17.02.22
Agenda
- Speck Schiffre
- CPA Angriffe
- CPA auf Speck
- Gegenmaßnahmen
- Hiding
Speck
- Symmentrische ARX Schiffre
- Add/Rotate/XOR
- Entworfen von der NSA (Zusammen mit der Schiffre Simon)
- Performant in Hard-/Software
- Speck bietet mehrere mögliche Modis
- Anzahl Runden, Schlüssellänge, Blocklänge
- Paper: Simon and Speck: Block Ciphers for the Internet of Things
Speck - Setups
| Speck | Blocklänge | Schlüssellänge | Runden |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speck3264 | 32 Bit | 64 Bit | 22 |
| Speck4872 | 48 Bit | 72 Bit | 22 |
| Speck4896 | 48 Bit | 96 Bit | 23 |
| Speck6496 | 64 Bit | 96 Bit | 26 |
| Speck64128 | 64 Bit | 128 Bit | 27 |
| Speck9696 | 96 Bit | 96 Bit | 28 |
| Speck96144 | 96 Bit | 144 Bit | 29 |
| Speck128128 | 128 Bit | 128 Bit | 32 |
| Speck128192 | 128 Bit | 192 Bit | 33 |
| Speck1281256 | 128 Bit | 256 Bit | 34 |
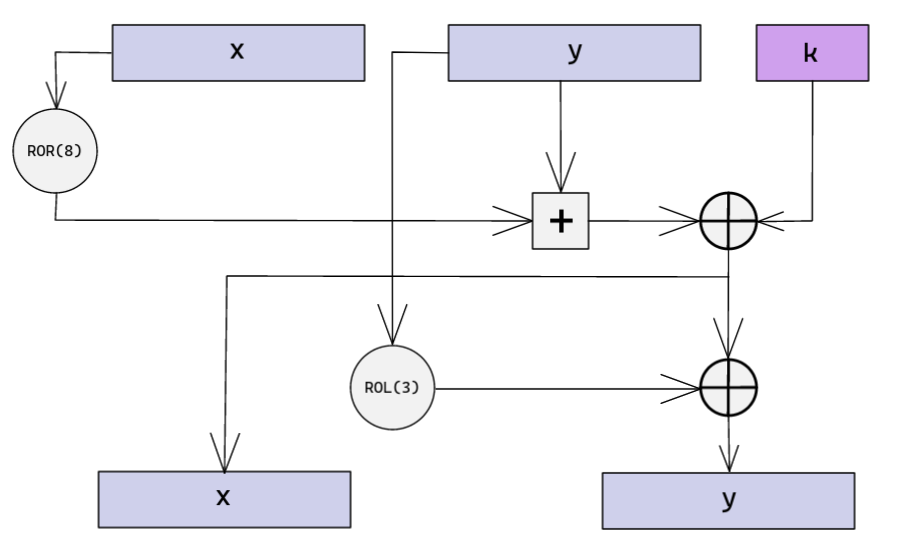
Speck - Rundenfunktion
- Wird während der Key Schedule aufgerufen
- Wird beim der Verschlüsselung aufgerufen
Speck - Pseudocode
pt = Plaintext Bytes Pt = Plaintext as 16 Bit Words
ct = Ciphertext Bytes Ct = Ciphertext as 16 Bit Words
k = Key as Bytes K = Key as 16 Bit Words
// Key Schedule
D=K[3], C=K[2], B=K[1], A=K[0]
for i in 0..<22
rk[i]=A
ER16(B, A, i++)
rk[i]=A
ER16(C, A, i++)
rk[i]=A
ER16(D, A, i++)
// Encryption
Ct[0]=Pt[0]; Ct[1]=Pt[1];
for i in 0..<22
ER16(Ct[1], Ct[0], rk[i++])
Speck - Möglicher Angriff
- Angriff der Rundenfunktion
- ADD/XOR/ROT Operationen
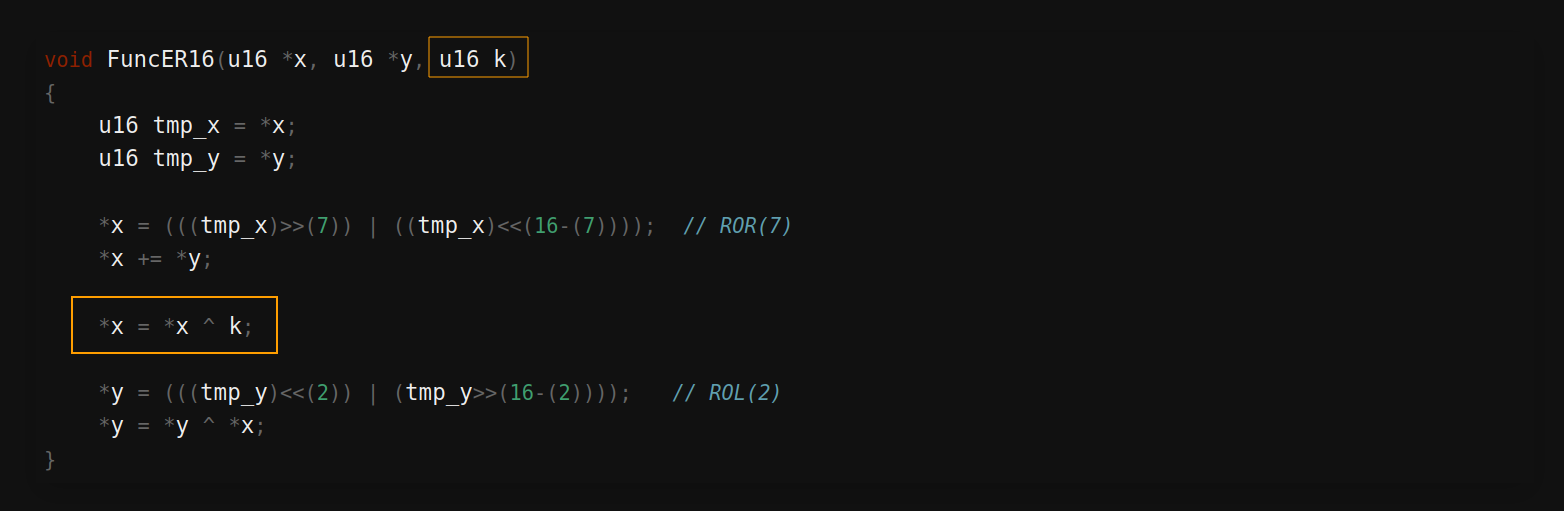
void FuncER16(u16 *x, u16 *y, u16 k)
{
u16 tmp_x = *x;
u16 tmp_y = *y;
*x = (((tmp_x)>>(7)) | ((tmp_x)<<(16-(7)))); // ROR(7)
*x += *y;
*x = *x ^ k;
*y = (((tmp_y)<<(2)) | (tmp_y>>(16-(2)))); // ROL(2)
*y = *y ^ *x;
}
Speck - Möglicher Angriff
- Der Rundenschlüssel steckt in der XOR Operation:
Correlation Power Analysis
- Variante von Differential Power Analysis (DPA)
- Nutzt Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC)
- Bei Speck: Korrelation zwischen Power-Trace und Rundenschlüssel
- Vorgehen:
- Modell erstellen
- Finden der Korrelationen im Modell
- Anwenden auf Hardware Implementierung
Hamming Weight
- Passendes Modell zum 'bewerten' des Stromverbrauchs
- Chip hat ein gewissen Basisverbrauch (IDLE)
- Werden Bytes im Chip verändert ($0 \rightarrow 1 ; 1 \rightarrow 0$) wird Strom benötigt
- Verhalten kann durch die Hamming-Distanz simuliert werden
- Hamming Distanz: Anzahl der Veränderter Bits:
$$HammingDistance(0100101, 0010101) = 2$$
Der Unterschied zweier per XOR verknüpfter Daten, wird als Hamming-Gewicht bezeichnet:
$$HammingDistance(0100101, 0010101) = HammingWeight(0100101 \oplus 0010101)$$
Speck - Modell
- Einfaches Modell der Speck Verschlüsselung
- Kann für die ersten 2 Byte des Rundenschlüssels genutzt werden:
def simple_speck(plaintext, key):
Ct_0 = (int(plaintext[1]) << 8) + int(plaintext[0]) # RIGHT Key
Ct_1 = (int(plaintext[3]) << 8) + int(plaintext[2]) # LEFT Key
Ct_1, Ct_0 = ER16(Ct_1, Ct_0, key) # Calculate Roundfunction
return popcount((Ct_1 << 8) + Ct_0) # Return Hamming Weight (aka Popcount)
Speck - Simulation
0) Simulation anhand des Modells mit $n$ traces 1) Generieren von $n$ zufälligen Klartexten mit fixem Keybyte (+ noise) 2) Simulation aller möglichen Keybytes per Hamming Weight 3) Berechnen des PCC aller Keys über alle traces
$\rightarrow$ Das korrekte Keybyte ist: 0x68
T-Test
- Wird verwendet um Leakage zu erkennen
- Gibt das Berechnen einer Chiffre mehr Information zurück als geplant: Leakage
- Ausnutzbar z.B. durch die Power Traces
- Berechnet durch:
- Vergleicht zwei unabhängige Stichproben miteinander, und vergleicht Mittelwerte
- Je unterschiedlicher die Mittelwerte $\rightarrow$ desto weniger Leakage
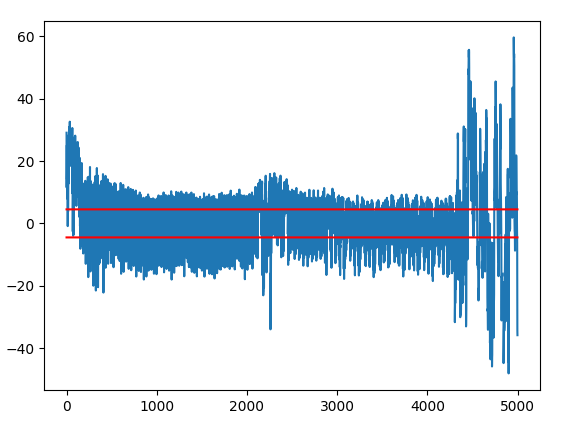
T-Test
- T-Test der aufgezeichneten Power-Traces:
Angriff - Hardware
1) Implementierung von Speck auf CW 2) Aufzeichnen von $n$ Power Traces 3) Berechnung des Software Modells 4) Berechnen der Korrelationen zwischen Modell/Powertraces
- Keybyte für Keybyte
- Rückrechnen des Rundenschlüssels
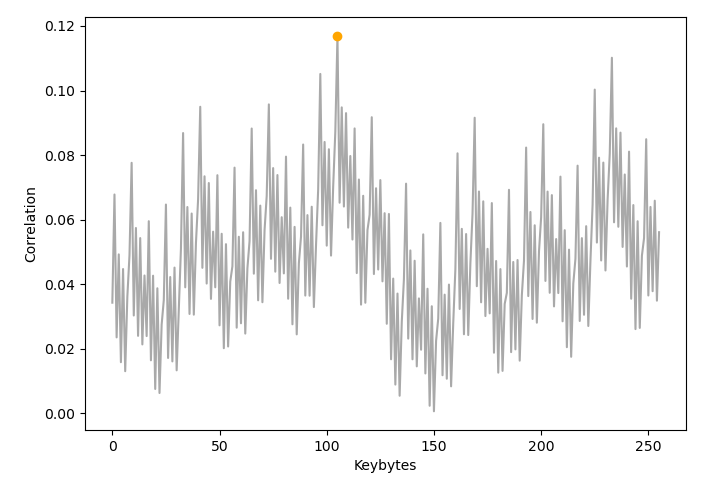
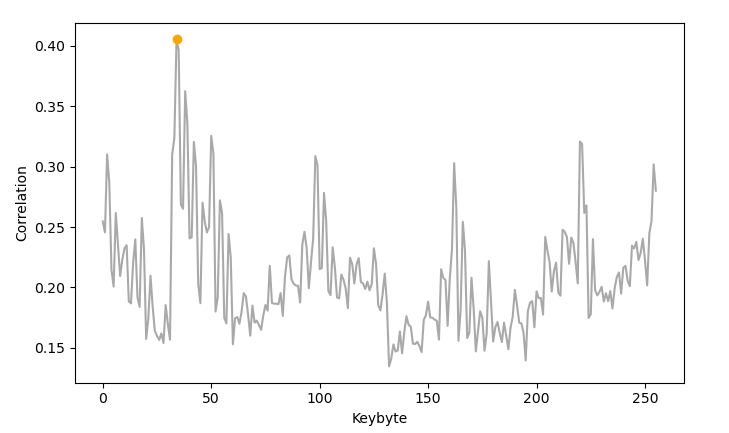
Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes
- Correlationen des ersten Keybytes
- Korrelation fällt höher aus als im Modell
- Deutliches Maximum der Korrelation bei 0x22 (Korrektes Keybyte)
Problem: Blocksize
- Bei Speck1632: Operationen nicht auf Byte sondern auf 16-Bit Ebene
- Erste Idee: Modell und Korrelation auf $2^16$ Keys
- $\rightarrow$ Keyspace ist abdeckbar (65536 Keys)
- $\rightarrow$ Zu langsam, Unschön
- $\rightarrow$ Nicht möglich für andere Modis von Speck (32 Bit Subkeys)
- Lösung: Modell funktioniert auch auf allen Teilbytes per Shift:
rightkey = 0x00
for guess_key in range(256):
leftkey = model( (guess_key << 8) + righkey )
for guess_key in range(256):
rightkey = model( (leftkey << 8) + guess_key )
- Auch umsetzbar auf Speck mit Blocksize > 16 Bit
Problem: $n^{th}$ Keybytes
- Modell kann nur für die ersten zwei Keybytes genutzt werden, da:
for i in 0..<22
ER16(Ct[1], Ct[0], rk[i++])
- Die (bereits bekannten) Rundenkeys müssen miteingeschlossen werden
- Muss an der richtigen Stelle passieren ($\oplus$-Operation)
Problem: $n^{th}$ Keybytes
- Anpassung des Modells:
# -------------- for one key -----------------#
x = ((x << (16 - ALPHA)) + (x >> ALPHA)) & mod_mask # x = ROR(x, 7)
x = (x + y) & mod_mask # x = ADD(x, y)
x = x ^ knownkey[0]
# -------------- for second key -----------------#
y = ((y >> (16 - BETA)) + (y << BETA)) & mod_mask # y = ROL(y, 2)
y = y ^ x # y = XOR(y, x)
x = ((x << (16 - ALPHA)) + (x >> ALPHA)) & mod_mask # x = ROR(x, 7)
x = (x + y) & mod_mask # x = ADD(x, y)
x = x ^ knownkey[1] # x = XOR(x, k)
# -------------- for third key -----------------#
# [...]
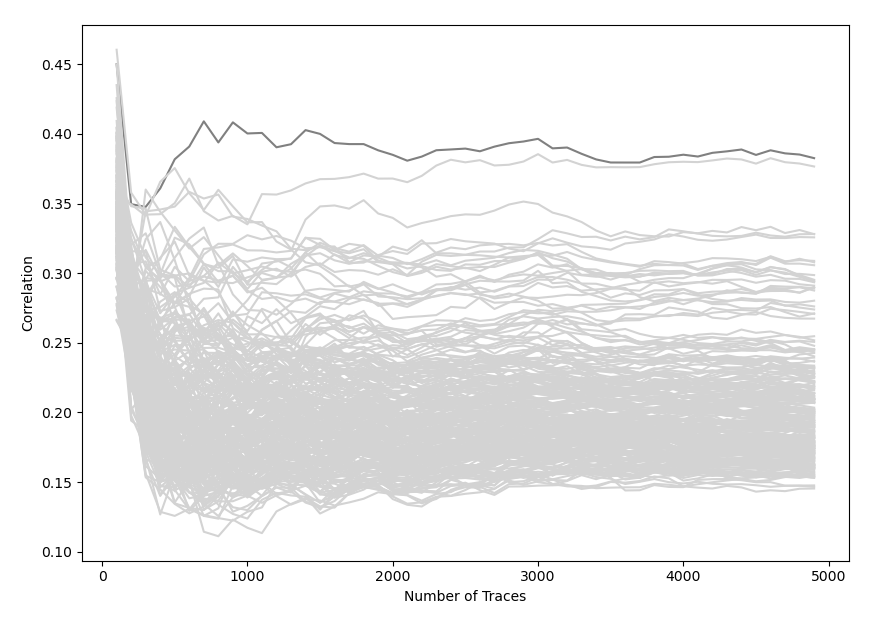
Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes
- Graph zeigt die Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes bis 5000 traces
- Ab ~800 Traces hebt sich die Korrelation deutlich hervor
Gegenmaßnahmen
Hiding
- Verstecken des eigentlichen "Leakages" in Rauschen
- $\rightarrow$ Erhöhung des vorhandenen Rauschens während der Berechnung
- Mehrere Möglichkeiten
- Mischen der Instruction-Order
- Hinzufügen von "Dummy Instructionen"
- Clock Jitter
Hiding - Code
- Ansatz: Korrelation kommt von
ER16()- Add/XOR/Rotate
- Hinzufügen weitere AXR Operationen um noise zu erhöhen
- Ersetzen von jeder XOR Operatione mit folgender:
uint16_t XOR(uint16_t a, uint16_t b, int random) {
uint8_t tmp = random ^ 0x5F;
tmp ^= (random ^ a);
tmp ^= (tmp ^ b);
tmp &= (tmp & a);
tmp &= (tmp & b);
return a ^ b;
}
Randomwird bei jeder Verschlüsslung erneut generiert
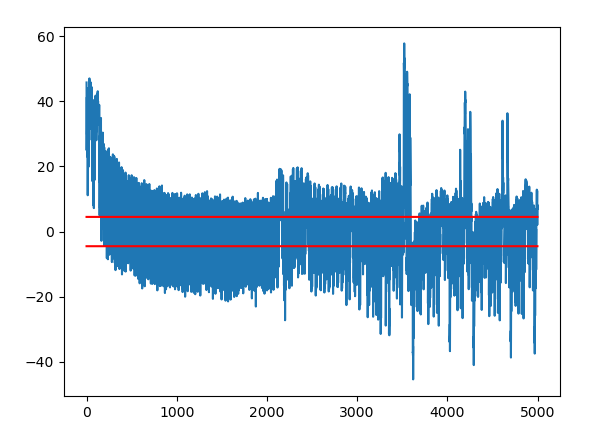
Hiding - T-Test
- Ergebnisse des T-Tests mit implementierter Hiding Maßnahmen:
- Bedarf weitere Analysen, Unterschied der beiden T-Tests sind nur Minimal
- Keine Indikation dass Hiding funktioniert laut T-Test
Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes
- Besseres Ergbniss der Korrelationen bis 5000 Traces
- Korrelationen flachen ab ~800 drastisch ab
- Keine Korrelation sticht heraus
- Es war nicht möglich den Angriff erneut durchzuführen
- Neue Korrelationen nach einigen Test lediglich bei ~0.18 mit falschem Keybyte
Hiding (Potentieller) Bypass
- Korrelation sollte weiterhin möglich sein wenn man die Operationen in Betracht zieht
- Schwierigkeit hängt am Zufallszahlengenerator
- Problem: Sichere Zufallszahlen auf Embedded Chips ist nicht trivial
$\rightarrow$ Bypass konnte nicht realisiert werden
Referenzen
- Improved Differential Cryptanalysis of Round-Reduced Speck
- Breaking Speck cryptosystem using correlation power analysis attack
- Speck-R: An ultra light-weight cryptographic scheme for Internet of Things