|
|
@@ -1,645 +0,0 @@
|
|
|
-<!DOCTYPE html>
|
|
|
-<html>
|
|
|
-<head>
|
|
|
- <meta charset="utf-8">
|
|
|
- <meta name="generator" content="pandoc">
|
|
|
- <meta name="author" content="Robin Dietrich & Marius Schwarz">
|
|
|
- <title>Implementation Attacks</title>
|
|
|
- <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes">
|
|
|
- <meta name="apple-mobile-web-app-status-bar-style" content="black-translucent">
|
|
|
- <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=no, minimal-ui">
|
|
|
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="./reveal.js/dist/reset.css">
|
|
|
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="./reveal.js/dist/reveal.css">
|
|
|
- <style>
|
|
|
- code{white-space: pre-wrap;}
|
|
|
- span.smallcaps{font-variant: small-caps;}
|
|
|
- span.underline{text-decoration: underline;}
|
|
|
- div.column{display: inline-block; vertical-align: top; width: 50%;}
|
|
|
- div.hanging-indent{margin-left: 1.5em; text-indent: -1.5em;}
|
|
|
- ul.task-list{list-style: none;}
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre; position: relative; }
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode > span { display: inline-block; line-height: 1.25; }
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode > span:empty { height: 1.2em; }
|
|
|
- .sourceCode { overflow: visible; }
|
|
|
- code.sourceCode > span { color: inherit; text-decoration: inherit; }
|
|
|
- div.sourceCode { margin: 1em 0; }
|
|
|
- pre.sourceCode { margin: 0; }
|
|
|
- @media screen {
|
|
|
- div.sourceCode { overflow: auto; }
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- @media print {
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode { white-space: pre-wrap; }
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode > span { text-indent: -5em; padding-left: 5em; }
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- pre.numberSource code
|
|
|
- { counter-reset: source-line 0; }
|
|
|
- pre.numberSource code > span
|
|
|
- { position: relative; left: -4em; counter-increment: source-line; }
|
|
|
- pre.numberSource code > span > a:first-child::before
|
|
|
- { content: counter(source-line);
|
|
|
- position: relative; left: -1em; text-align: right; vertical-align: baseline;
|
|
|
- border: none; display: inline-block;
|
|
|
- -webkit-touch-callout: none; -webkit-user-select: none;
|
|
|
- -khtml-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none;
|
|
|
- -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
|
|
|
- padding: 0 4px; width: 4em;
|
|
|
- color: #aaaaaa;
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- pre.numberSource { margin-left: 3em; border-left: 1px solid #aaaaaa; padding-left: 4px; }
|
|
|
- div.sourceCode
|
|
|
- { }
|
|
|
- @media screen {
|
|
|
- pre > code.sourceCode > span > a:first-child::before { text-decoration: underline; }
|
|
|
- }
|
|
|
- code span.al { color: #ff0000; font-weight: bold; } /* Alert */
|
|
|
- code span.an { color: #60a0b0; font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; } /* Annotation */
|
|
|
- code span.at { color: #7d9029; } /* Attribute */
|
|
|
- code span.bn { color: #40a070; } /* BaseN */
|
|
|
- code span.bu { } /* BuiltIn */
|
|
|
- code span.cf { color: #007020; font-weight: bold; } /* ControlFlow */
|
|
|
- code span.ch { color: #4070a0; } /* Char */
|
|
|
- code span.cn { color: #880000; } /* Constant */
|
|
|
- code span.co { color: #60a0b0; font-style: italic; } /* Comment */
|
|
|
- code span.cv { color: #60a0b0; font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; } /* CommentVar */
|
|
|
- code span.do { color: #ba2121; font-style: italic; } /* Documentation */
|
|
|
- code span.dt { color: #902000; } /* DataType */
|
|
|
- code span.dv { color: #40a070; } /* DecVal */
|
|
|
- code span.er { color: #ff0000; font-weight: bold; } /* Error */
|
|
|
- code span.ex { } /* Extension */
|
|
|
- code span.fl { color: #40a070; } /* Float */
|
|
|
- code span.fu { color: #06287e; } /* Function */
|
|
|
- code span.im { } /* Import */
|
|
|
- code span.in { color: #60a0b0; font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; } /* Information */
|
|
|
- code span.kw { color: #007020; font-weight: bold; } /* Keyword */
|
|
|
- code span.op { color: #666666; } /* Operator */
|
|
|
- code span.ot { color: #007020; } /* Other */
|
|
|
- code span.pp { color: #bc7a00; } /* Preprocessor */
|
|
|
- code span.sc { color: #4070a0; } /* SpecialChar */
|
|
|
- code span.ss { color: #bb6688; } /* SpecialString */
|
|
|
- code span.st { color: #4070a0; } /* String */
|
|
|
- code span.va { color: #19177c; } /* Variable */
|
|
|
- code span.vs { color: #4070a0; } /* VerbatimString */
|
|
|
- code span.wa { color: #60a0b0; font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; } /* Warning */
|
|
|
- .display.math{display: block; text-align: center; margin: 0.5rem auto;}
|
|
|
- </style>
|
|
|
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="./reveal.js/dist/theme/night.css" id="theme">
|
|
|
- <link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/custom.css"/>
|
|
|
-</head>
|
|
|
-<body>
|
|
|
- <div class="reveal">
|
|
|
- <div class="slides">
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-<section id="title-slide">
|
|
|
- <h1 class="title">Implementation Attacks</h1>
|
|
|
- <p class="author">Robin Dietrich & Marius Schwarz</p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-<section id="agenda" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Agenda</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Einleitung</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Seitenkanalangriffe</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Speck</li>
|
|
|
-<li>CPA Angriffe</li>
|
|
|
-<li>CPA auf Speck</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Gegenmaßnahmen</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Hiding</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="bedeutung-von-seitenkanalangriffen" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Bedeutung von Seitenkanalangriffen</h1>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="voraussetzungen-für-erfolgreichen-angriff" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Voraussetzungen für erfolgreichen Angriff</h1>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Symmentrische ARX Schiffre
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Add/Rotate/XOR</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-<li>Entworfen von der NSA (Zusammen mit der Schiffre Simon)</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Performant in Hard-/Software</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Speck bietet mehrere mögliche Modis
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Anzahl Runden, Schlüssellänge, Blocklänge</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-<li>Paper: <a href="https://csrc.nist.gov/csrc/media/events/lightweight-cryptography-workshop-2015/documents/papers/session1-shors-paper.pdf">Simon and Speck: Block Ciphers for the Internet of Things</a></li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---setups" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Setups</h1>
|
|
|
-<table>
|
|
|
-<thead>
|
|
|
-<tr class="header">
|
|
|
-<th>Speck</th>
|
|
|
-<th>Blocklänge</th>
|
|
|
-<th>Schlüssellänge</th>
|
|
|
-<th>Runden</th>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-</thead>
|
|
|
-<tbody>
|
|
|
-<tr class="odd">
|
|
|
-<td><span style="color:#d08a1d"><strong>Speck3264</strong></span></td>
|
|
|
-<td><span style="color:#d08a1d"><strong>32 Bit</strong></span></td>
|
|
|
-<td><span style="color:#d08a1d"><strong>64 Bit</strong></span></td>
|
|
|
-<td><span style="color:#d08a1d"><strong>22</strong></span></td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="even">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck4872</td>
|
|
|
-<td>48 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>72 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>22</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="odd">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck4896</td>
|
|
|
-<td>48 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>96 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>23</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="even">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck6496</td>
|
|
|
-<td>64 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>96 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>26</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="odd">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck64128</td>
|
|
|
-<td>64 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>128 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>27</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="even">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck9696</td>
|
|
|
-<td>96 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>96 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>28</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="odd">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck96144</td>
|
|
|
-<td>96 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>144 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>29</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="even">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck128128</td>
|
|
|
-<td>128 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>128 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>32</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="odd">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck128192</td>
|
|
|
-<td>128 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>192 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>33</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-<tr class="even">
|
|
|
-<td>Speck1281256</td>
|
|
|
-<td>128 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>256 Bit</td>
|
|
|
-<td>34</td>
|
|
|
-</tr>
|
|
|
-</tbody>
|
|
|
-</table>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---rundenfunktion" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Rundenfunktion</h1>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/rundenfunktion.png" width="400" /></p>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Wird während der Key Schedule aufgerufen</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Wird beim der Verschlüsselung aufgerufen</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---pseudocode" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Pseudocode</h1>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb1"><pre class="sourceCode c"><code class="sourceCode c"><span id="cb1-1"><a href="#cb1-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>pt <span class="op">=</span> Plaintext Bytes Pt <span class="op">=</span> Plaintext as <span class="dv">16</span> Bit Words</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-2"><a href="#cb1-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>ct <span class="op">=</span> Ciphertext Bytes Ct <span class="op">=</span> Ciphertext as <span class="dv">16</span> Bit Words</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-3"><a href="#cb1-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>k <span class="op">=</span> Key as Bytes K <span class="op">=</span> Key as <span class="dv">16</span> Bit Words</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-4"><a href="#cb1-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-5"><a href="#cb1-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="co">// Key Schedule</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-6"><a href="#cb1-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>D<span class="op">=</span>K<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">3</span><span class="op">],</span> C<span class="op">=</span>K<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">2</span><span class="op">],</span> B<span class="op">=</span>K<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">1</span><span class="op">],</span> A<span class="op">=</span>K<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">0</span><span class="op">]</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-7"><a href="#cb1-7" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-8"><a href="#cb1-8" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="cf">for</span> i in <span class="fl">0.</span><span class="er">.</span><span class="op"><</span><span class="dv">22</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-9"><a href="#cb1-9" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> rk<span class="op">[</span>i<span class="op">]=</span>A</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-10"><a href="#cb1-10" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> ER16<span class="op">(</span>B<span class="op">,</span> A<span class="op">,</span> i<span class="op">++)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-11"><a href="#cb1-11" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> rk<span class="op">[</span>i<span class="op">]=</span>A</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-12"><a href="#cb1-12" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> ER16<span class="op">(</span>C<span class="op">,</span> A<span class="op">,</span> i<span class="op">++)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-13"><a href="#cb1-13" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> rk<span class="op">[</span>i<span class="op">]=</span>A</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-14"><a href="#cb1-14" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> ER16<span class="op">(</span>D<span class="op">,</span> A<span class="op">,</span> i<span class="op">++)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-15"><a href="#cb1-15" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-16"><a href="#cb1-16" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="co">// Encryption</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-17"><a href="#cb1-17" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">0</span><span class="op">]=</span>Pt<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">0</span><span class="op">];</span> Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">1</span><span class="op">]=</span>Pt<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">1</span><span class="op">];</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-18"><a href="#cb1-18" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-19"><a href="#cb1-19" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="cf">for</span> i in <span class="fl">0.</span><span class="er">.</span><span class="op"><</span><span class="dv">22</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb1-20"><a href="#cb1-20" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> ER16<span class="op">(</span>Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">1</span><span class="op">],</span> Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">0</span><span class="op">],</span> rk<span class="op">[</span>i<span class="op">++])</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---möglicher-angriff" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Möglicher Angriff</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Angriff der Rundenfunktion</li>
|
|
|
-<li>ADD/XOR/ROT Operationen</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb2"><pre class="sourceCode c"><code class="sourceCode c"><span id="cb2-1"><a href="#cb2-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="dt">void</span> FuncER16<span class="op">(</span>u16 <span class="op">*</span>x<span class="op">,</span> u16 <span class="op">*</span>y<span class="op">,</span> u16 k<span class="op">)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-2"><a href="#cb2-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="op">{</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-3"><a href="#cb2-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> u16 tmp_x <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">*</span>x<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-4"><a href="#cb2-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> u16 tmp_y <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">*</span>y<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-5"><a href="#cb2-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-6"><a href="#cb2-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="op">*</span>x <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">(((</span>tmp_x<span class="op">)>>(</span><span class="dv">7</span><span class="op">))</span> <span class="op">|</span> <span class="op">((</span>tmp_x<span class="op">)<<(</span><span class="dv">16</span><span class="op">-(</span><span class="dv">7</span><span class="op">))));</span> <span class="co">// ROR(7)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-7"><a href="#cb2-7" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="op">*</span>x <span class="op">+=</span> <span class="op">*</span>y<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-8"><a href="#cb2-8" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-9"><a href="#cb2-9" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="op">*</span>x <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">*</span>x <span class="op">^</span> k<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-10"><a href="#cb2-10" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-11"><a href="#cb2-11" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="op">*</span>y <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">(((</span>tmp_y<span class="op">)<<(</span><span class="dv">2</span><span class="op">))</span> <span class="op">|</span> <span class="op">(</span>tmp_y<span class="op">>>(</span><span class="dv">16</span><span class="op">-(</span><span class="dv">2</span><span class="op">))));</span> <span class="co">// ROL(2)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-12"><a href="#cb2-12" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="op">*</span>y <span class="op">=</span> <span class="op">*</span>y <span class="op">^</span> <span class="op">*</span>x<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb2-13"><a href="#cb2-13" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="op">}</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---möglicher-angriff-1" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Möglicher Angriff</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Der Rundenschlüssel steckt in der XOR Operation</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/er16_enc_rk.png" /> <img data-src="img/er16_annot.png" /></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="correlation-power-analysis" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Correlation Power Analysis</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Variante von Differential Power Analysis (DPA)</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Nutzt Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC)</li>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Bei Speck:</strong> Korrelation zwischen Power-Trace und Rundenschlüssel</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Vorgehen:
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Modell erstellen</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Finden der Korrelationen im Modell</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Anwenden auf Hardware Implementierung</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="theoretischer-angriff" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Theoretischer Angriff</h1>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="hamming-weight" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Hamming Weight</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Passendes Modell zum ‘bewerten’ des Stromverbrauchs</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Chip hat ein gewissen Basisverbrauch (IDLE)</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Werden Bytes im Chip verändert (<span class="math inline">0 → 1; 1 → 0</span>) wird Strom benötigt</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Verhalten kann durch die Hamming-Distanz simuliert werden</li>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Hamming Distanz:</strong> Anzahl der Veränderter Bits:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><span class="math display"><em>H</em><em>a</em><em>m</em><em>m</em><em>i</em><em>n</em><em>g</em><em>D</em><em>i</em><em>s</em><em>t</em><em>a</em><em>n</em><em>c</em><em>e</em>(0100101,0010101) = 2</span></p>
|
|
|
-<p>Der Unterschied zweier per XOR verknüpfter Daten, wird als Hamming-Gewicht bezeichnet:</p>
|
|
|
-<p><span class="math display"><em>H</em><em>a</em><em>m</em><em>m</em><em>i</em><em>n</em><em>g</em><em>D</em><em>i</em><em>s</em><em>t</em><em>a</em><em>n</em><em>c</em><em>e</em>(0100101,0010101) = <em>H</em><em>a</em><em>m</em><em>m</em><em>i</em><em>n</em><em>g</em><em>W</em><em>e</em><em>i</em><em>g</em><em>h</em><em>t</em>(0100101⊕0010101)</span></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="speck---modell" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Speck - Modell</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Einfaches Modell der Speck Verschlüsselung</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Kann für die ersten 2 Byte des Rundenschlüssels genutzt werden:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb3"><pre class="sourceCode python"><code class="sourceCode python"><span id="cb3-1"><a href="#cb3-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="kw">def</span> simple_speck(plaintext, key):</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-2"><a href="#cb3-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> Ct_0 <span class="op">=</span> (<span class="bu">int</span>(plaintext[<span class="dv">1</span>]) <span class="op"><<</span> <span class="dv">8</span>) <span class="op">+</span> <span class="bu">int</span>(plaintext[<span class="dv">0</span>]) <span class="co"># RIGHT Key</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-3"><a href="#cb3-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> Ct_1 <span class="op">=</span> (<span class="bu">int</span>(plaintext[<span class="dv">3</span>]) <span class="op"><<</span> <span class="dv">8</span>) <span class="op">+</span> <span class="bu">int</span>(plaintext[<span class="dv">2</span>]) <span class="co"># LEFT Key</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-4"><a href="#cb3-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-5"><a href="#cb3-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> Ct_1, Ct_0 <span class="op">=</span> ER16(Ct_1, Ct_0, key) <span class="co"># Calculate Roundfunction</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-6"><a href="#cb3-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb3-7"><a href="#cb3-7" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="cf">return</span> popcount((Ct_1 <span class="op"><<</span> <span class="dv">8</span>) <span class="op">+</span> Ct_0) <span class="co"># Return Hamming Wight (aka Popcount)</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="t-test" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>T-Test</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Wird verwendet um <em>Leakage</em> zu erkennen
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Gibt das Berechnen einer Chiffre mehr Information zurück als geplant: Leakage</li>
|
|
|
-<li>z.B. durch die Power Traces</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-<li>Berechnet durch:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/ttest_calc.png" /></p>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Vergleicht zwei unabhängige Stichproben miteinander, und vergleicht Mittelwerte</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Je unterschiedlicher die Mittelwerte <span class="math inline">→</span> desto weniger Leakage</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="t-test-1" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>T-Test</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>T-Test der aufgezeichneten Power-Traces:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/t_test_original.png" /></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="angriff" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Angriff</h1>
|
|
|
-<ol type="1">
|
|
|
-<li>Implementierung von Speck auf CW</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Aufzeichnen von X PowerTraces</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Berechnung des Software Modells</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Berechnen der Korrelationen zwischen Modell/Powertraces
|
|
|
-<ol type="1">
|
|
|
-<li>Keybyte für Keybyte</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Rückrechnen des Rundenschlüssels</li>
|
|
|
-</ol></li>
|
|
|
-</ol>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="korrelationen-des-ersten-keybytes" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
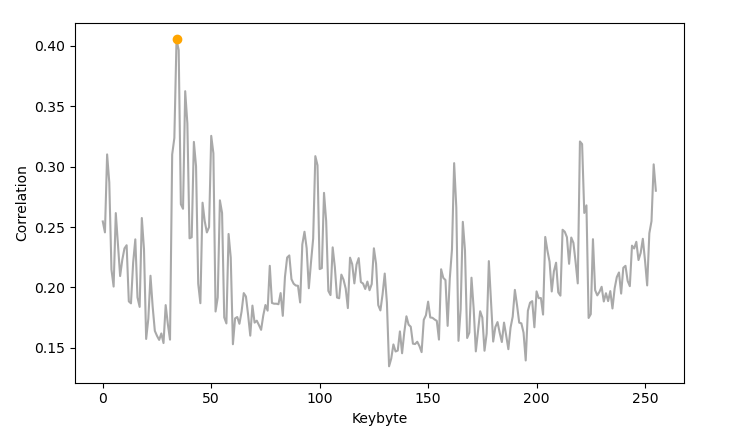
-<h1>Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Correlationen des ersten Keybytes</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Deutliches Maximum der Korrelation bei 0x11</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/correlation_keybyte.png" width="550" /></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="problem-blocksize" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Problem: Blocksize</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Bei <strong>Speck1632:</strong> Operationen nicht auf Byte sondern auf 16-Bit Ebene</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Erste Idee: Modell und Korrelation auf <span class="math inline">2<sup>16</sup></span> Keys</li>
|
|
|
-<li><span class="math inline">→</span> Zu langsam, Unschön</li>
|
|
|
-<li><span class="math inline">→</span> Nicht möglich für andere Modis von Speck</li>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Lösung:</strong> Modell funktioniert auch auf allen Teilbytes:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb4"><pre class="sourceCode python"><code class="sourceCode python"><span id="cb4-1"><a href="#cb4-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a>rightkey <span class="op">=</span> <span class="bn">0x00</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb4-2"><a href="#cb4-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="cf">for</span> guess_key <span class="kw">in</span> <span class="bu">range</span>(<span class="dv">256</span>):</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb4-3"><a href="#cb4-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> leftkey <span class="op">=</span> model( (guess_key <span class="op"><<</span> <span class="dv">8</span>) <span class="op">+</span> righkey )</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb4-4"><a href="#cb4-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb4-5"><a href="#cb4-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="cf">for</span> guess_key <span class="kw">in</span> <span class="bu">range</span>(<span class="dv">256</span>):</span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb4-6"><a href="#cb4-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> rightkey <span class="op">=</span> model( (leftkey <span class="op"><<</span> <span class="dv">8</span>) <span class="op">+</span> guess_key )</span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Auch umsetzbar auf Speck mit Blocksize > 16 Bit</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="problem-nth-keybytes" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Problem: <span class="math inline"><em>n</em><sup><em>t</em><em>h</em></sup></span> Keybytes</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Modell kann nur für die ersten zwei Keybytes genutzt werden, da:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb5"><pre class="sourceCode c"><code class="sourceCode c"><span id="cb5-1"><a href="#cb5-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="cf">for</span> i in <span class="fl">0.</span><span class="er">.</span><span class="op"><</span><span class="dv">22</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb5-2"><a href="#cb5-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> ER16<span class="op">(</span>Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">1</span><span class="op">],</span> Ct<span class="op">[</span><span class="dv">0</span><span class="op">],</span> rk<span class="op">[</span>i<span class="op">++])</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Die Rundenkeys zuvor müssen miteingeschlossen werden</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Muss an der richtigen Stelle passieren (<span class="math inline">⊕</span>-Operation)</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="problem-nth-keybytes-1" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Problem: <span class="math inline"><em>n</em><sup><em>t</em><em>h</em></sup></span> Keybytes</h1>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb6"><pre class="sourceCode python"><code class="sourceCode python"><span id="cb6-1"><a href="#cb6-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="co"># -------------- for one key -----------------#</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-2"><a href="#cb6-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> ((x <span class="op"><<</span> (<span class="dv">16</span> <span class="op">-</span> ALPHA)) <span class="op">+</span> (x <span class="op">>></span> ALPHA)) <span class="op">&</span> mod_mask <span class="co"># x = ROR(x, 7)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-3"><a href="#cb6-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> (x <span class="op">+</span> y) <span class="op">&</span> mod_mask <span class="co"># x = ADD(x, y)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-4"><a href="#cb6-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-5"><a href="#cb6-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> x <span class="op">^</span> knownkey[<span class="dv">0</span>] </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-6"><a href="#cb6-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-7"><a href="#cb6-7" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="co"># -------------- for second key -----------------#</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-8"><a href="#cb6-8" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-9"><a href="#cb6-9" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> y <span class="op">=</span> ((y <span class="op">>></span> (<span class="dv">16</span> <span class="op">-</span> BETA)) <span class="op">+</span> (y <span class="op"><<</span> BETA)) <span class="op">&</span> mod_mask <span class="co"># y = ROL(y, 2)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-10"><a href="#cb6-10" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> y <span class="op">=</span> y <span class="op">^</span> x <span class="co"># y = XOR(y, x)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-11"><a href="#cb6-11" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> ((x <span class="op"><<</span> (<span class="dv">16</span> <span class="op">-</span> ALPHA)) <span class="op">+</span> (x <span class="op">>></span> ALPHA)) <span class="op">&</span> mod_mask <span class="co"># x = ROR(x, 7)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-12"><a href="#cb6-12" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> (x <span class="op">+</span> y) <span class="op">&</span> mod_mask <span class="co"># x = ADD(x, y)</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-13"><a href="#cb6-13" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-14"><a href="#cb6-14" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> x <span class="op">=</span> x <span class="op">^</span> knownkey[<span class="dv">1</span>] <span class="co"># x = XOR(x, k) </span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-15"><a href="#cb6-15" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> </span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-16"><a href="#cb6-16" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="co"># -------------- for third key -----------------#</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb6-17"><a href="#cb6-17" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="co"># [...]</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="korrelationen-des-ersten-keybytes-1" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
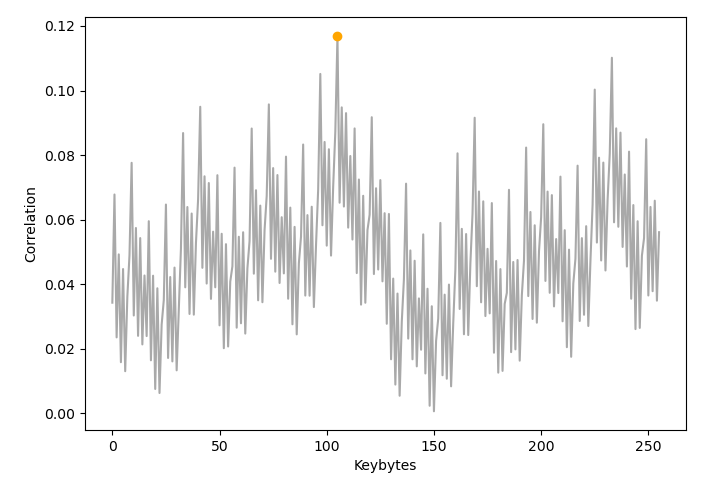
-<h1>Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes</h1>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/traces.png" width="550" /></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="gegenmaßnahmen" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Gegenmaßnahmen</h1>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="hiding" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Hiding</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Verstecken des eigentlichen “Leakages” in Rauschen</li>
|
|
|
-<li><span class="math inline">→</span> Erhöhung des vorhandenen Rauschens während der Berechnung</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Mehrere Möglichkeiten
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Mischen der Instruction-Order</li>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Hinzufügen von “Dummy Instructionen”</strong></li>
|
|
|
-<li>Clock Jitter</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="hiding---code" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Hiding - Code</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Ansatz:</strong> Korrelation kommt von <code>ER16()</code>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>XOR/Add/Rotate</li>
|
|
|
-</ul></li>
|
|
|
-<li>Hinzufügen weitere RXA Operationen um Noice zu erhöhen</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Ersetzen von jeder XOR Operatione mit folgender:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<div class="sourceCode" id="cb7"><pre class="sourceCode c"><code class="sourceCode c"><span id="cb7-1"><a href="#cb7-1" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="dt">uint16_t</span> XOR<span class="op">(</span><span class="dt">uint16_t</span> a<span class="op">,</span> <span class="dt">uint16_t</span> b<span class="op">,</span> <span class="dt">int</span> random<span class="op">)</span> <span class="op">{</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-2"><a href="#cb7-2" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="dt">uint8_t</span> tmp <span class="op">=</span> random <span class="op">^</span> <span class="bn">0x5F</span><span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-3"><a href="#cb7-3" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> tmp <span class="op">^=</span> <span class="op">(</span>random <span class="op">^</span> a<span class="op">);</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-4"><a href="#cb7-4" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> tmp <span class="op">^=</span> <span class="op">(</span>tmp <span class="op">^</span> b<span class="op">);</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-5"><a href="#cb7-5" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> tmp <span class="op">&=</span> <span class="op">(</span>tmp <span class="op">&</span> a<span class="op">);</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-6"><a href="#cb7-6" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> tmp <span class="op">&=</span> <span class="op">(</span>tmp <span class="op">&</span> b<span class="op">);</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-7"><a href="#cb7-7" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a> <span class="cf">return</span> a <span class="op">^</span> b<span class="op">;</span></span>
|
|
|
-<span id="cb7-8"><a href="#cb7-8" aria-hidden="true" tabindex="-1"></a><span class="op">}</span></span></code></pre></div>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Random wird bei jeder Verschlüsslung erneut generiert</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="hiding---t-test" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Hiding - T-Test</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Ergebnisse des T-Tests mit implementierter Hiding Maßnahmen:</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/t_test_hiding_random.png" /></p>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Bedarf weitere Analysen, Unterschied der beiden T-Tests sind nur Minimal</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Keine Indikation dass Hiding funktioniert</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="korrelationen-des-ersten-keybytes-2" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Korrelationen des ersten Keybytes</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Besseres Ergbniss der Korrelationen bis 5000 Traces</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Keine Korrelation sticht heraus</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><img data-src="img/corr_traces_hiding_5k.png" width="550" /></p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="hiding-bypass" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Hiding Bypass</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li>Korrelation sollte weiterhin möglich sein wenn man die Operationen in Betracht zieht</li>
|
|
|
-<li>Schwierigkeit hängt am Zufallszahlengenerator</li>
|
|
|
-<li><strong>Problem:</strong> Sichere Zufallszahlen auf Embedded Chips ist nicht trivial</li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-<p><span class="math inline">→</span> Bypass konnte <strong>nicht</strong> realisiert werden</p>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
-<section id="referenzen" class="slide level1">
|
|
|
-<h1>Referenzen</h1>
|
|
|
-<ul>
|
|
|
-<li><a href="Improved%20Differential%20Cryptanalysis%20of%20Round-Reduced%20Speck">Improved Differential Cryptanalysis of Round-Reduced Speck</a></li>
|
|
|
-<li><a href="Breaking%20Speck%20cryptosystem%20using%20correlation%20power%20analysis%20attack">Breaking Speck cryptosystem using correlation power analysis attack</a></li>
|
|
|
-<li><a href="%7BSpeck-R:%20An%20ultra%20light-weight%20cryptographic%20scheme%20for%20Internet%20of%20Things">{Speck-R: An ultra light-weight cryptographic scheme for Internet of Things</a></li>
|
|
|
-</ul>
|
|
|
-</section>
|
|
|
- </div>
|
|
|
- </div>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <script src="./reveal.js/dist/reveal.js"></script>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <!-- reveal.js plugins -->
|
|
|
- <script src="./reveal.js/plugin/notes/notes.js"></script>
|
|
|
- <script src="./reveal.js/plugin/search/search.js"></script>
|
|
|
- <script src="./reveal.js/plugin/zoom/zoom.js"></script>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- <script>
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Full list of configuration options available at:
|
|
|
- // https://revealjs.com/config/
|
|
|
- Reveal.initialize({
|
|
|
- // Display controls in the bottom right corner
|
|
|
- controls: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Help the user learn the controls by providing hints, for example by
|
|
|
- // bouncing the down arrow when they first encounter a vertical slide
|
|
|
- controlsTutorial: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Determines where controls appear, "edges" or "bottom-right"
|
|
|
- controlsLayout: 'bottom-right',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Visibility rule for backwards navigation arrows; "faded", "hidden"
|
|
|
- // or "visible"
|
|
|
- controlsBackArrows: 'faded',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Display a presentation progress bar
|
|
|
- progress: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Display the page number of the current slide
|
|
|
- slideNumber: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // 'all', 'print', or 'speaker'
|
|
|
- showSlideNumber: 'all',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Add the current slide number to the URL hash so that reloading the
|
|
|
- // page/copying the URL will return you to the same slide
|
|
|
- hash: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Start with 1 for the hash rather than 0
|
|
|
- hashOneBasedIndex: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags if we should monitor the hash and change slides accordingly
|
|
|
- respondToHashChanges: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Push each slide change to the browser history
|
|
|
- history: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Enable keyboard shortcuts for navigation
|
|
|
- keyboard: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Enable the slide overview mode
|
|
|
- overview: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Disables the default reveal.js slide layout (scaling and centering)
|
|
|
- // so that you can use custom CSS layout
|
|
|
- disableLayout: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Vertical centering of slides
|
|
|
- center: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Enables touch navigation on devices with touch input
|
|
|
- touch: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Loop the presentation
|
|
|
- loop: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Change the presentation direction to be RTL
|
|
|
- rtl: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // see https://revealjs.com/vertical-slides/#navigation-mode
|
|
|
- navigationMode: 'default',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Randomizes the order of slides each time the presentation loads
|
|
|
- shuffle: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Turns fragments on and off globally
|
|
|
- fragments: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags whether to include the current fragment in the URL,
|
|
|
- // so that reloading brings you to the same fragment position
|
|
|
- fragmentInURL: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags if the presentation is running in an embedded mode,
|
|
|
- // i.e. contained within a limited portion of the screen
|
|
|
- embedded: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags if we should show a help overlay when the questionmark
|
|
|
- // key is pressed
|
|
|
- help: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags if it should be possible to pause the presentation (blackout)
|
|
|
- pause: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Flags if speaker notes should be visible to all viewers
|
|
|
- showNotes: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Global override for autoplaying embedded media (null/true/false)
|
|
|
- autoPlayMedia: null,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Global override for preloading lazy-loaded iframes (null/true/false)
|
|
|
- preloadIframes: null,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Number of milliseconds between automatically proceeding to the
|
|
|
- // next slide, disabled when set to 0, this value can be overwritten
|
|
|
- // by using a data-autoslide attribute on your slides
|
|
|
- autoSlide: 0,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Stop auto-sliding after user input
|
|
|
- autoSlideStoppable: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Use this method for navigation when auto-sliding
|
|
|
- autoSlideMethod: null,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Specify the average time in seconds that you think you will spend
|
|
|
- // presenting each slide. This is used to show a pacing timer in the
|
|
|
- // speaker view
|
|
|
- defaultTiming: null,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Enable slide navigation via mouse wheel
|
|
|
- mouseWheel: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // The display mode that will be used to show slides
|
|
|
- display: 'block',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Hide cursor if inactive
|
|
|
- hideInactiveCursor: true,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Time before the cursor is hidden (in ms)
|
|
|
- hideCursorTime: 5000,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Opens links in an iframe preview overlay
|
|
|
- previewLinks: false,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Transition style (none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom)
|
|
|
- transition: 'slide',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Transition speed (default/fast/slow)
|
|
|
- transitionSpeed: 'default',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Transition style for full page slide backgrounds
|
|
|
- // (none/fade/slide/convex/concave/zoom)
|
|
|
- backgroundTransition: 'fade',
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Number of slides away from the current that are visible
|
|
|
- viewDistance: 3,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // Number of slides away from the current that are visible on mobile
|
|
|
- // devices. It is advisable to set this to a lower number than
|
|
|
- // viewDistance in order to save resources.
|
|
|
- mobileViewDistance: 2,
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
- // reveal.js plugins
|
|
|
- plugins: [
|
|
|
- RevealNotes,
|
|
|
- RevealSearch,
|
|
|
- RevealZoom
|
|
|
- ]
|
|
|
- });
|
|
|
- </script>
|
|
|
- </body>
|
|
|
-</html>
|